When it comes to fortifying online privacy and security, individuals often consider proxies or VPNs. Despite both aiming to shield identities on the web, they function distinctively. Nevertheless, many users interchangeably utilize them without fully grasping their disparities.
To elucidate the differences between proxies and VPNs and aid users in making informed decisions, it's essential to comprehend the basics of each. Proxies and VPNs both act as intermediaries between a user's device and the internet. They reroute traffic through external servers to conceal the user's IP address and encrypt data. However, their methodologies diverge significantly.
Proxies serve as middlemen, relaying user requests to websites on their behalf. While they provide anonymity by masking IP addresses, they usually offer limited encryption beyond basic protocols like HTTPS. Proxies are commonly employed for specific tasks, such as accessing geo-blocked content or managing multiple social media accounts. Conversely, VPNs establish secure, encrypted connections between a user's device and a remote server operated by the VPN provider. This encrypted tunnel shields user data, ensuring privacy and security. VPNs are preferred for comprehensive online protection, particularly when accessing sensitive information or using public Wi-Fi networks. Understanding these distinctions can assist users in selecting the most suitable solution for their browsing requirements.
Understanding Proxies
A proxy server acts as a mediator between a client and a server, possessing a distinct IP address in a location chosen by the user. When a user requests a resource, like a web page, the request initially goes to the proxy server, which then forwards it to the intended destination server. Similarly, it retrieves the resource on behalf of the client.
This process ensures that the user's IP address remains concealed, safeguarding their online identity and privacy. This feature proves beneficial for various purposes, such as enhancing anonymity, circumventing geographical restrictions on content, or accessing websites barred by network administrators. To explore additional use cases, you can refer to our blog post on the diverse applications of proxies.
Understanding VPNs
Much like proxies, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) reroutes your internet traffic through a private server before directing it to its intended online destination. By doing so, it masks your internet traffic as if it originated from a different IP address. However, VPNs go a step further by encrypting your traffic, thereby ensuring a heightened level of security.
When you install a VPN on your device, it funnels all your internet traffic through it. While proxies can achieve a similar effect, they also offer the flexibility to set up traffic redirection for specific apps or browsers, allowing you to use your own IP address for other activities. Consequently, while VPNs provide a uniform solution, proxies boast a more diverse functionality.
Although certain types of proxies may support encryption, it's essential to consider that VPNs are explicitly designed with encryption in mind. While this enhances online security, particularly when accessing public Wi-Fi networks, it does come with some drawbacks that users should bear in mind when weighing the pros and cons of proxies versus VPNs.
Proxy vs. VPN – Similarities and Differences
Given that 8 out of 10 individuals express concerns about online privacy, it's unsurprising that both proxies and VPNs enjoy widespread popularity. While these tools may seem capable of achieving similar ends, they employ distinct approaches. Depending on your specific requirements, you may find one preferable to the other.
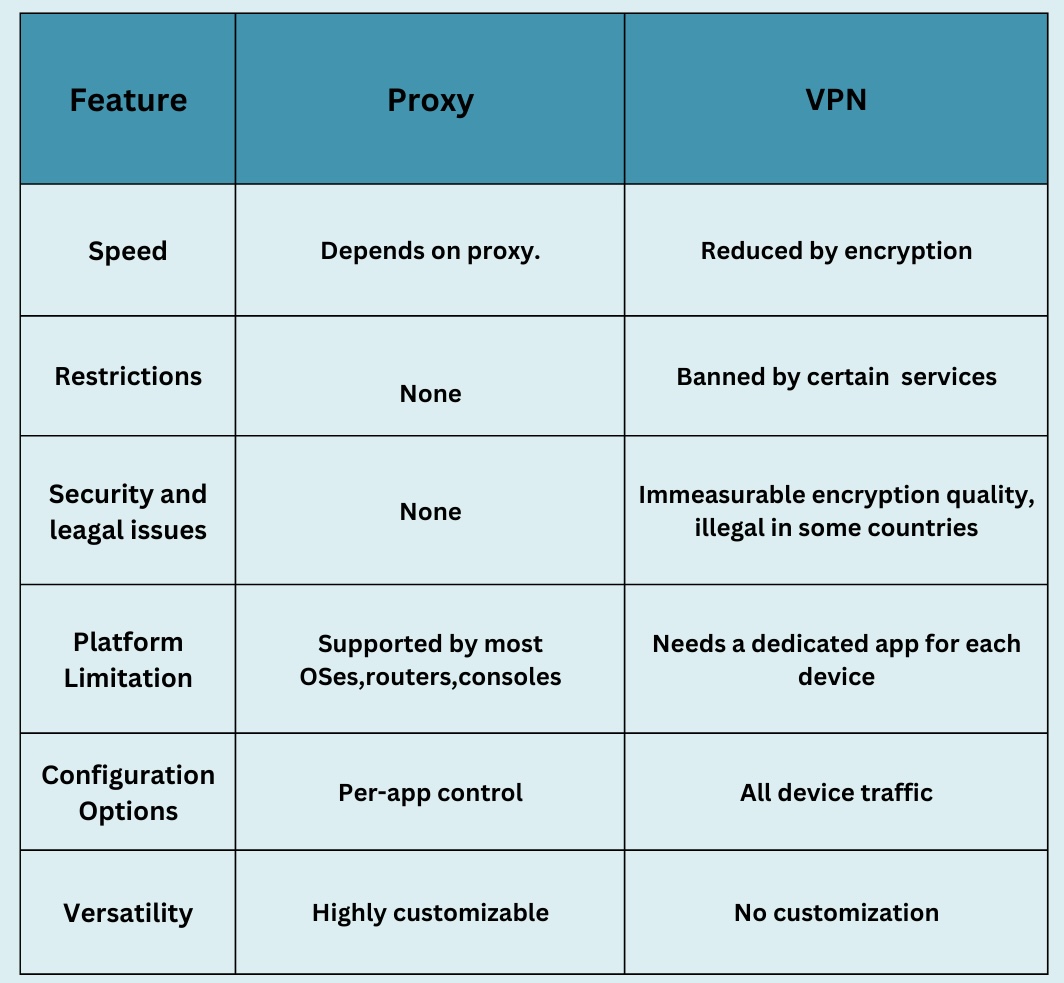
In terms of their shared attributes, both proxies and VPNs conceal your real IP address, thereby enhancing online anonymity and privacy. Now, let's examine their differences across several key aspects:
- Ease of use:
VPNs typically offer greater ease of setup and usage, as they are tailored for individual users. In contrast, proxies are more geared towards business and professional usage scenarios, such as web scraping, ad verification, and SEO research. Consequently, proxies may be better suited for business applications, while VPNs may be more suitable for average internet users lacking technical expertise.
- Security and speed:
While encrypting your traffic enhances connection security, it often comes at the expense of internet speed. VPNs consistently encrypt data, ensuring network security but potentially slowing down your connection. Conversely, proxies alleviate concerns about slowdowns, making them ideal for activities requiring high bandwidth and low latency, such as streaming, video conferencing, and gaming.
- Configuration options and versatility:
Installing a VPN on your device channels all traffic through it. In contrast, proxies offer the flexibility to configure traffic redirection for individual apps or browsers, allowing you to use your own IP address for other purposes. Thus, while VPNs provide a standardized solution, proxies offer a broader range of functionalities.
- Restrictions:
Both proxies and VPNs enable users to appear as though they are accessing content from a different location, facilitating access to region-restricted content. However, certain websites, games, and streaming platforms may prohibit the use of VPNs. In such cases, proxies, which utilize IPs from real users and ISPs, may serve as the preferred solution.
Final Thoughts
There's no definitive winner in the proxy versus VPN debate. Both options effectively safeguard your IP address and enhance online privacy. The choice between proxies and VPNs hinges on your specific requirements. Regardless of your decision, it's essential to conduct thorough research and opt for a reputable provider with a proven track record of reliability.

